Devices for wound closure consist of specially designed staples, sutures, and mechanical tools that help in the closure of wounds by bringing the edges of the wound tissue closer together.
These devices come in various designs and may require adjustment of pressure or tension after application to a patient, or they may be designed to absorb into the skin, depending on their function and manufacturing. They may be recommended for use on traumatic, chronic, and surgical wounds, as well as on flaps and skin grafts.
How to Use the Wound Closure Device?
1. Get the Skin Ready
Double-check that the areas for adhesion are free of foreign materials or blood. Cleanse the skin with alcohol and wait for it to dry completely. Depending on the surgeon’s preference, hair clipping may be required. This is because the device’s adhesion to oily skin or hair-bearing may be inadequate.
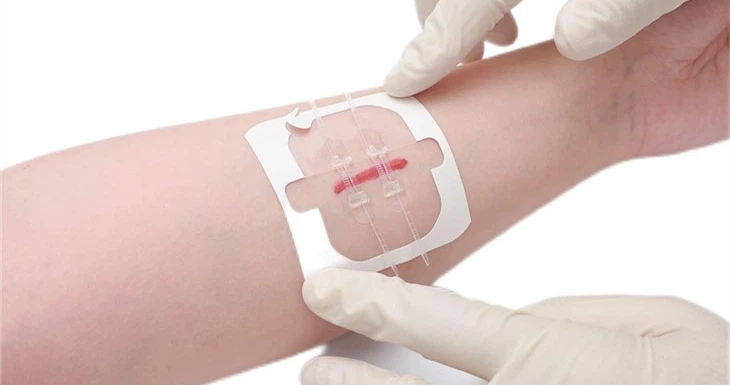
2. Stick the Strips
Peel off the protective strip from the adhesive located beneath the rigid plastic area featuring two holes. Place this section directly over the wound. Remove the backing from the rest of the strip and affix it onto the skin. Apply pressure to the strip to guarantee proper adhesion.
3. Retention Suture
Execute a substantial full-depth bite using a non-absorbable suture on both sides of the wound through one of the perforations in the wound closure device. A larger gauge (e.g., nylon 2-0 or larger) is most suitable. The tension in the suture ends should be adjusted to bring the wound edges together based on the surgeon’s preference.
4. Complete the Closure
To support the wound closure device, a layered closure is suggested. This should encompass buried absorbable sutures and some form of top closure, such as sutures, staples, glue, sterile strips, and others.
Benefits of the Wound Closure Device
- The wound closure device aids in the natural healing process by bringing together the edges of the wound. Surgical wound closure brings the tissue layers into direct contact, reducing the formation of new tissue within the wound.
- It is a viable alternative to intricate reconstruction for particular surgical defects. This technique also hinges on the four stages of wound healing to accomplish the final result.
Conclusion
Across various medical specialties, procedures, and surgical patients, wound closure devices have a profound impact. They are instrumental in improving patient outcomes, accelerating the healing process, and optimizing the efficiency of operating rooms. Pick one today to lessen the risk of surgical site infections!

